Industry research
Scope
US
Companies
113
Table of contents
What does the space tech market landscape look like in the US?
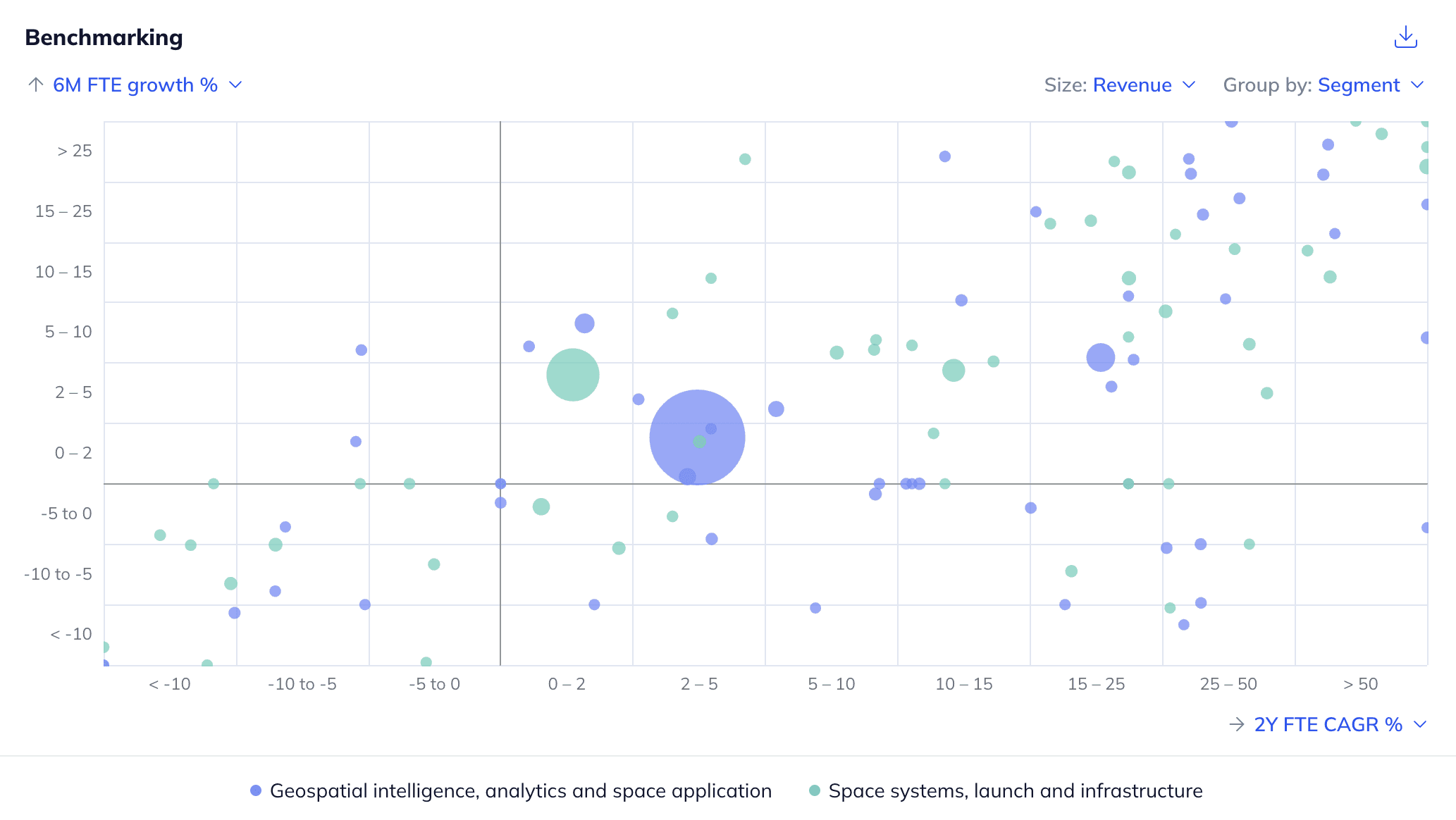
The US SpaceTech market exhibits varying levels of consolidation. In the space systems, launch and infrastructure segment, SpaceX has a monopoly over the orbital launches, capturing ~95% of all US launches, while Apex Space and K2 Space stand out as leading satellite bus manufacturers. The geospatial intelligence, analytics and space application segment is relatively less consolidated, with a handful of leaders dominating specific niches. Depending on the scale of operations, buy versus build has been an important operational decision-making criterion. While SpaceX and Blue Origin chose to manufacture in-house, EOS DATA ANALYTICS and Phantom Space rely on external manufacturers.
What is the level of investor activity in the US's space tech industry?
Investor interest in this segment has been notable, with ~50% of identified assets being backed by financial sponsors (November 2025). Investors in this space are attracted to (i) increasing defense and civilian applications, (ii) rapid technological advancements leading to reduced costs and (iii) a favorable regulatory environment. On the other hand, (i) uncertainty around scalability potential amidst increased R&D costs, (ii) geopolitical and supply concerns affecting operations and (iii) persistent labor shortage in highly skilled areas act as detractors.
What are the key ESG considerations in the US's space tech industry?
ESG topics in the US SpaceTech industry primarily revolve around environmental factors. Challenges include orbital debris, high launch emissions, hazardous propellant waste, energy-intensive infrastructure and reliance on unsustainably sourced rare earth raw materials. Remedies focus on reusable systems to reduce waste, cleaner propellants, efficiency gains across manufacturing and ground operations, shifts to renewable energy and stronger oversight that audits supply chains, tracks material lifecycle impact and enforces responsible sourcing.
The global space economy was valued at ~$630.0bn in 2023 and is forecasted to reach ~$1.8tn by 2035 (+9.1% CAGR 2023-2035; McKinsey & Company, April 2024)
The global space exploration market will be valued at ~$100bn in 2025 and is expected to reach ~$135bn by 2029 (+7% CAGR 2025‑2029; Technavio, November 2025)
Rapid advancements in AI-driven satellite operations, in-orbit servicing, 3D printing and propulsion technology will accelerate space capabilities across constellation management, real-time data analytics, on-orbit assembly and orbital logistics. These innovations reduce operational costs, extend satellite lifespans and broaden demand across various industries, helping the production of high-value materials in space, in-orbit refueling, debris mitigation and rapid deployment of specialized satellite services (PwC, April 2025; Innovation Network, February 2025)
Increasing government funding, policy support and strategic defense investment will bolster demand as federal agencies continue to prioritize space assets, R&D and domestic manufacturing to maintain technological leadership. To illustrate, the US Space Force increased its FY2025 budget to ~$28.8bn, with leadership calling for ~20% additional growth, signaling sustained demand for space programs (Deloitte, June 2025; Space Insider, May 2025)
Accelerating demand for space-based connectivity and low-earth-orbit (LEO) broadband for global internet coverage, rural access and new IoT networks. This will create significant opportunities in satellite manufacturing, launch services, ground terminal infrastructure and spectrum management while enabling next-generation applications such as real-time Earth observation, smart city connectivity, autonomous vehicle navigation and resilient communication networks for defense and disaster response (IISS, May 2025; Goldman Sachs, March 2025; BCG; March 2024)
Launch congestion and overcapacity risk weaken low Earth orbit (LEO) economics. Rapid launch growth creates orbital crowding while aggressive constellation buildouts outpace demand and pressure unit pricing. Elevated collision risk drives up insurance premiums and liability exposure while requiring more costly debris mitigation systems, enhanced space traffic coordination and continuous servicing, slowing deployment timelines and raising operational costs.(Insurance Business, June 2025; BCG, June 2025)
Intensifying geopolitical tensions and international competition will increasingly constrain market share growth and squeeze profit margins for US space companies. As nation-states (e.g. China, Russia) dramatically expand their space investments, the risk of stricter export controls, satellite interference, restricted orbital slot access and targeted cyberattacks on critical space infrastructure could materially disrupt operations (BCG, June 2025; Space Tech Expo, February 2025; Reuters, October 2024)
Growing talent shortages could constrain growth and delay commercialization timelines. Additionally, national security hiring restrictions that require US citizenship or security clearances further limit the candidate pool, slowing project timelines, inflating recruitment and training costs, and constraining innovation capacity (Space Foundation, April 2025; Space News, September 2024)
With the full report, you’ll gain access to:
Detailed assessments of the market outlook
Insights from c-suite industry executives
A clear overview of all active investors in the industry
An in-depth look into 113 private companies, incl. financials, ownership details and more.
A view on all 451 deals in the industry
ESG assessments with highlighted ESG outperformers







